Chapter 5: Large Projects
5.4: The Port of Zeebrugge and the East Coast Project (Belgium) (1)

| European Coasts - An Introductory Survey Chapter 5: Large Projects 5.4: The Port of Zeebrugge and the East Coast Project (Belgium) (1) |
|
 |
 |
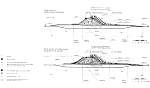 |
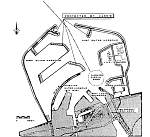
| Fig 123: Port of Zeebrugge with "old" western mole | Fig 124: Lay-out of new harbour | Fig 125: Cross-sections of the breakwater |
Zeebrugge has had a small port since about 1900 (see Fig. 123). It was extended considerably during the 1970s (see also Fig. 124). The old west mole was "surrounded" by the new breakwater; the old east mole was removed and replaced by a new one. The harbour area was enlarged and the inland connections were improved. Fig. 125 and Fig. 126 provide an overview of the construction of the breakwaters. Fig. 125 shows typical cross-sections of the new breakwater. Grooved cubes and HARO blocks (see Fig. 127) were used as armour units.
The detailed design specified a breakwater foundation involving soil replacement by dredging of unsuitable topsoils and the dumping of selected sand as backfill. The dumped sand had to reach a mean static cone resistance value of 5 MN/m2. Where this value was not obtained, compaction in depth based on vertical vibration was applied. Explosive compaction was employed for the head of the NW-breakwater.
Hydraulic and sedimentation studies indicated that erosion of the foundation bed could be expected in front of the breakwater. A detailed programme of bottom protection was designed, consisting respectively of a layer of gravel, willow mattresses and stone filter layers. In such a large project, huge amounts of material were used. More than 1 million m2 of willow mattresses were placed. Stone was supplied by 23 different quarries in Belgium; 10 million tonnes of stone was transported to Zeebrugge. Six million tonnes were supplied by trucks, involving 300,000 truck loads. Circa 70,000 concrete armour units were fabricated and placed to protect the breakwaters.
previous page table of contents next page
| This page is from the book "European Coasts", produced in the framework of the Erasmus project under EC contract ICP 92-G-2013 and placed on the Internet in the framework of the PIANC-MarCom initiative on Education. |