 PIANC Open Teaching Material
PIANC Open Teaching Material

clm010722.jpg
Terminology of a rocky coast with shingle beach (fig 11 from "European Coasts")

clm010723.jpg
Terminology of a mud coast (fig 14 from "European Coasts")

clm010724.jpg
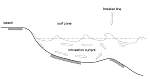
The island of Skye, Scotland, is separated from the mainland by the sound of Sleat formed by glaciers during the Ice Age, UK, fig 18 from "European Coasts"

clm010725.jpg
Sandy pocket beach at Santa Teresa, Gallura, Sardinia, Italy (fig. 25 from "European Coasts")
clm010726.jpg
Tidal forces and the equilibrium tide (fig. 32 of European Coasts)
clm010727.jpg
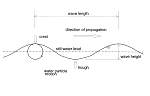
Definition of a sinusoidal wave (fig. 38 from European Coasts)

clm010728.jpg
The distribution of a measured irregular wave field (fig 39 of European Coasts)
clm010729.jpg
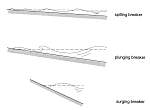
Typoes of breaking waves (fig. 42 from European Coasts)

clm010730.jpg
Wave refraction pattern. The wave crests start by approaching the coast obliquely but end up essentially parallel to the coast (fig. 45 from European Coasts)

clm010731.jpg
Record of the waterlevel at Vlissingen (Flushing, the Netherlands) during the 1953 storm surge (fig. 48 from European Coasts)
clm010732.jpg
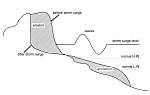
Erosion of a beach profile during a storm surge (fig. 49 from European Coasts)
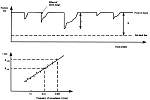
clm010733.jpg
Position of the coastline due to storm surges. Study of the position of the coastline can help to estimate the preservation distance (=R) which will be exceeded only with a chosen frequency (fig. 50 from European Coasts)
clm010734.jpg
The undertow which plays a role in cross-shore transport (fig. 51 from European Coasts)
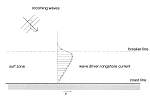
clm010735.jpg
The veloctity profile of the wave driven longshore current (fig. 53 from European Coasts)

clm010736.jpg
Raising operation around one of the Ekofisk platform legs (fig 66 from European Coasts, Hydraudyne, Boxtel)

clm010737.jpg
Shoreline rates of change along the Ebro delta (fig. 132 from European Coasts)

clm010741.jpg
Spilling breakers at the beach of Zanvoort, the Netherlands (fig. 43 from "European Coasts"
|
|||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | |||||