Chapter 4: Coastal structures
4.1 Breakwaters (2)

| European Coasts - An Introductory Survey Chapter 4: Coastal structures 4.1 Breakwaters (2) |
|
 |
 |
 |
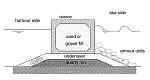
| Fig 75: Vertical breakwater constructed with circular caissons; Brighton marina, UK | Fig 76: Schematic illustration of a composite breakwater | Fig 77: Composite breakwater |
Vertical breakwaters (or monolithic breakwaters) use less material in deep water (see Fig. 74 and Fig. 75). However, the disadvantages of vertical breakwaters include the high reflectivity, with consequent toe scour and overtopping, and the high pressures on the foundation. Therefore they are used in relatively moderate wave conditions.
The composite breakwater combines the advantages of both previous types of breakwaters (see Fig. 76 and Fig. 77).
previous page table of contents next page
| This page is from the book "European Coasts", produced in the framework of the Erasmus project under EC contract ICP 92-G-2013 and placed on the Internet in the framework of the PIANC-MarCom initiative on Education. |